
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is no longer a simple game of bidding on keywords and hoping for the best. To truly connect with modern consumers, marketers must embrace a more nuanced approach. The digital landscape is dominated by on-the-go users who expect relevance and personalization at every touchpoint. This is where advanced SEM tactics become not just an advantage, but a necessity.
By layering mobile-first strategies, precise geo-targeting, and intelligent remarketing, you can transform your campaigns from broad-reaching broadcasts into highly relevant conversations.
This guide will explore how to master these three pillars of modern SEM. You will learn to create synergistic campaigns that reduce wasted ad spend, boost conversions, and deliver the right message to the right person, at the right time, in the right place.
What Is Mobile SEM Targeting?
Mobile SEM targeting involves tailoring your search engine marketing campaigns specifically for users on smartphones and tablets. It goes beyond simply ensuring your ads appear on mobile devices; it’s about optimizing every element of your campaign—from keywords to ad copy and landing pages—for the mobile experience.
The importance of a mobile-first approach is undeniable. Users behave differently on their phones, often conducting quick, location-based searches with immediate intent. Ignoring this behavior means missing out on a massive segment of your potential audience.
There are several ways to target mobile users:
- Device Targeting: You can choose to show ads exclusively on mobile phones, tablets, or desktops, or adjust bids to prioritize one over the others.
- Operating System (OS) Targeting: This allows you to target users based on their device’s OS, such as iOS or Android, which is particularly useful for promoting apps.
- App Usage Targeting: You can reach users who have previously installed your app or similar apps, ensuring your message is relevant to their interests.
To succeed in mobile SEM, you must monitor key metrics that reveal how these users interact with your ads and website. Keep a close eye on mobile Click-Through Rate (CTR), bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates to understand what’s working and where you need to optimize.
Deep Dive into Geo-Targeting

Geo-targeting is a powerful SEM tactic that allows you to display ads to users in specific geographic locations. This precision ensures your marketing budget is spent on audiences who can actually access your products or services.
Types of Geo-Targeting
The granularity of geo-targeting offers immense flexibility for campaign setup. Common methods include:
- Country, State, and City Targeting: The broadest forms of geo-targeting, useful for national or regional campaigns.
- ZIP Code Targeting: Narrows your focus to specific postal codes, ideal for businesses serving particular neighborhoods.
- Radius Targeting: Lets you draw a circle around a specific point—like your storefront—and target users within that radius.
- Pin Drop Targeting: In platforms like Google Ads, you can drop a pin on a map to create a custom target area.
Advanced Geo-Targeting Options
For marketers looking to gain a competitive edge, more advanced strategies are available:
- Geofencing: This involves setting up a virtual perimeter around a specific location. When a user enters this “fence,” they become eligible to see your ads. This is perfect for driving foot traffic to a retail store or event.
- Geo-conquesting: A competitive strategy where you set up a geofence around a competitor’s location. By doing this, you can serve targeted ads to their customers, enticing them with a better offer.
A crucial element of effective geo-targeting is localization. Simply translating ad copy isn’t enough. You must adapt your messaging to reflect local culture, dialects, and consumer habits. For example, an ad for a coffee shop in Miami might highlight “cafecito,” while the same ad in Seattle would focus on a different local coffee culture. This cultural adaptation makes your ads feel more authentic and resonant.
Mastering Remarketing Strategies
Remarketing, also known as retargeting, is the practice of serving ads to users who have previously interacted with your brand online. It’s a highly effective tactic because you are reaching a “warm” audience that has already shown interest in what you offer.
The basic premise is simple: a user visits your website, a cookie is placed in their browser, and as they browse other sites in the ad network, your ads are displayed to them, reminding them of your brand.
Types of Remarketing Audiences
You can create remarketing lists based on various user actions:
- All Site Visitors: A broad approach targeting anyone who has visited your website.
- Cart Abandoners: A high-intent group that added items to their cart but didn’t complete the purchase. Targeting them with a discount or free shipping can be very effective.
- App Users: Re-engage users who have downloaded your app but haven’t used it recently.
- Specific Page Visitors: Target users who viewed a particular product or service page, allowing for highly specific ad messaging.
Integrating Geo-Targeting with Remarketing
The real power comes when you combine remarketing with geo-targeting. For instance, a national retail brand could create a remarketing list of users who visited their website. Then, they could layer geo-targeting to show a special in-store promotion only to those users when they are physically near a brick-and-mortar location. This geo-driven remarketing connects online interest with offline action, creating a seamless customer journey.
Synergy: Mobile + Geo-Targeting + Remarketing
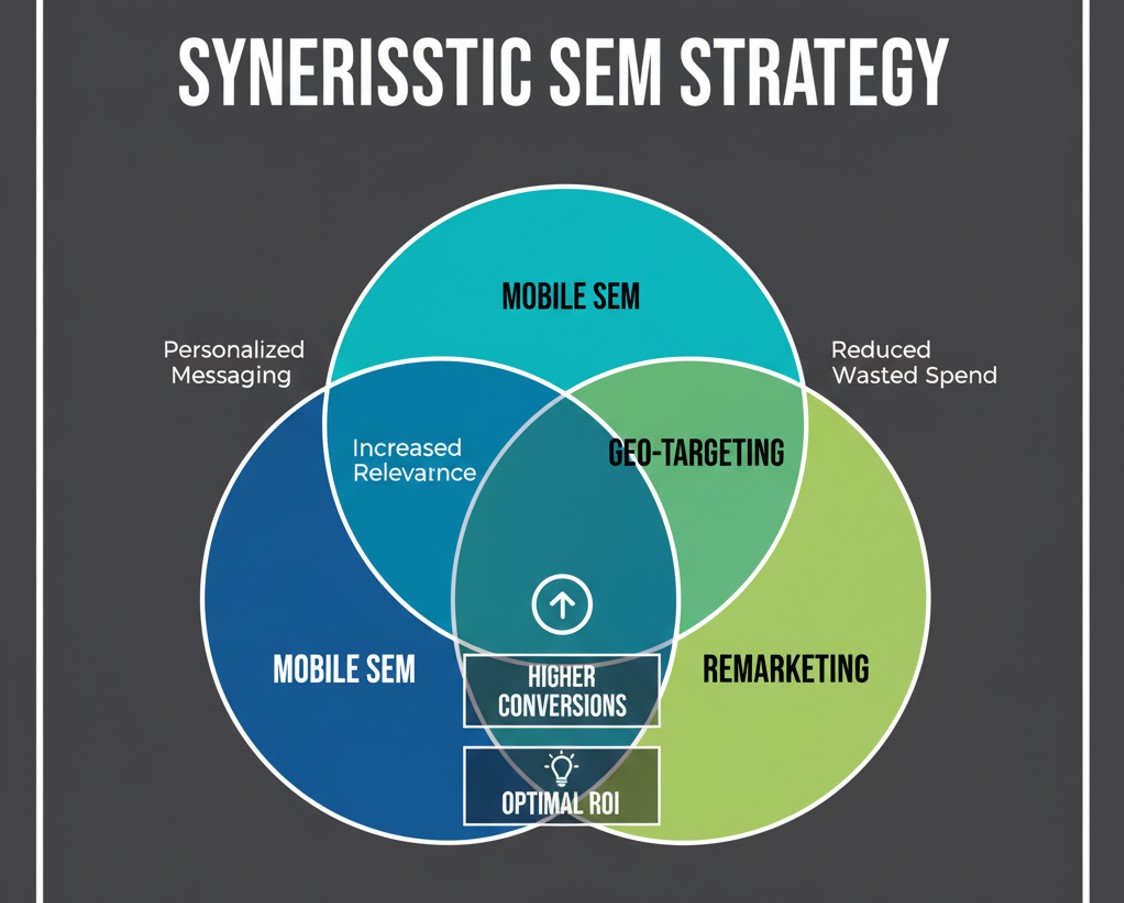
When used in isolation, each of these tactics is powerful. But when combined, they create a highly effective, synergistic SEM strategy that delivers unparalleled relevance and ROI.
Imagine these scenarios:
- A local restaurant wants to increase foot traffic during lunch hours. They can run a mobile-only campaign targeting users within a one-mile radius of their location between 11 AM and 2 PM. By layering remarketing, they can also serve a special “come back for a free drink” offer to past customers who are currently within that radius.
- A national retailer is having a weekend sale. They can use geofencing around their store locations to trigger a mobile ad notification to users on their remarketing list who enter the geofence. The ad could say, “You’re near our store! Pop in this weekend and get 20% off your purchase.”
- An e-commerce brand can create a remarketing campaign for cart abandoners. They can then use geo-targeting to adjust bids, bidding higher for users in regions with historically high conversion rates, ensuring their budget is allocated for maximum impact.
By weaving these three elements together, you reduce wasted spend by focusing only on the most relevant users, boost conversions with personalized and timely offers, and improve the overall customer experience.
Setting Up Your Advanced SEM Campaigns
Implementing these tactics requires careful setup in your chosen ad platform, such as Google Ads or Meta Ads.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Choose Your Platform: Google Ads is excellent for search intent and offers robust geo-targeting features. Meta (Facebook/Instagram) Ads excels at building remarketing audiences based on social interactions.
- Configure Geo-Targeting: In your campaign settings, navigate to the “Locations” section. You can add locations by country, city, or ZIP code. For more precision, use the “Radius” or “Advanced Search” options to pin-drop locations.
- Implement Device Targeting: Under “Devices,” you can set bid adjustments. For example, you might increase bids by 20% for mobile devices if they drive more conversions, or decrease bids for desktops if they underperform.
- Create Remarketing Audiences: In your platform’s audience manager, set up remarketing lists. You’ll need to install a tracking pixel or tag on your website to start collecting visitor data. Create segmented lists like “All Visitors,” “Product Viewers,” and “Cart Abandoners.”
- Layer Your Targeting: In your ad group settings, apply both your location targets and your remarketing audiences. This ensures your ads are only shown to users who meet both criteria.
Budgeting, Bidding, and Creative
- Budgeting: Allocate your budget based on performance. If mobile users in a specific city are converting at a high rate, dedicate more of your budget to that segment.
- Bidding: Use bid adjustments to prioritize high-value segments. Increase bids for mobile users near your store or for users on your cart abandonment list.
- Ad Creative: Tailor your ad creative for each segment. Use mobile-friendly formats like call extensions for easy dialing. Localize your ad copy with city names or local landmarks. Schedule ads to run at times of day when your target audience is most active.
Measuring Performance and Optimization
Launching the campaign is only the beginning. Continuous measurement and optimization are crucial for success.
Key Metrics to Monitor
Analyze performance by segment to understand what’s working:
- By Location: Compare CTR, CPC, Conversion Rate, Cost Per Acquisition (CPA), and Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) for different cities or regions.
- By Device: Break down these same metrics for mobile, desktop, and tablet to see how user behavior differs across devices.
Use this data to make informed decisions. If a particular city has a high CPA, consider reducing bids or pausing targeting there. If mobile devices have a much higher ROAS, reallocate more of your budget from desktop to mobile.
A/B Testing Strategies
Don’t rely on assumptions. Use A/B testing to find what truly resonates with your audience.
- Test Ad Creative: Split test different headlines and descriptions for each location.
- Test Landing Pages: See if a mobile-optimized landing page converts better than your standard page for mobile traffic.
- Test Offers: Try different promotions for your remarketing audiences to see which one drives the most conversions.
Challenges, Risks, and Best Practices
While powerful, these advanced tactics come with potential challenges.
- Technical Issues: Location data is not always perfect. GPS-based data is more accurate than IP-based data, but mobile connectivity issues can still lead to inaccuracies. Be aware of these limitations.
- Privacy Concerns: With regulations like GDPR and CCPA, user privacy is paramount. Be transparent about data usage and always obtain proper consent. Ensure your remarketing practices comply with all relevant laws.
- Avoid Over-Targeting: It can be tempting to create hyper-specific segments, but targeting an audience that is too narrow may limit your campaign’s reach and scale. Find the right balance between precision and volume.
- Ensure Localization Fits: A poorly executed localization effort can do more harm than good. Make sure your creative and messaging are culturally appropriate for each target region.
Case Study: Driving In-Store Sales for a Local Retailer
A boutique clothing store in Sacramento wanted to increase foot traffic and sales. They used an integrated mobile, geo-targeting, and remarketing strategy on Google Ads.
- Geo-Targeting: They set up a 5-mile radius target around their store.
- Mobile-First Bidding: They increased bids by 30% for searches made on mobile devices within that radius.
- Remarketing: They created a remarketing list of everyone who had visited their website in the past 30 days.
- Synergy: They launched a campaign targeting users on their remarketing list who were currently on a mobile device and within the 5-mile geofence. The ad featured a special offer: “Show this ad in-store for 15% off your purchase today!”
The results were impressive. The campaign led to a 40% increase in in-store foot traffic attributed to the ads and a ROAS of 8:1. By reaching interested customers when they were nearby and ready to shop, the store turned digital interest into tangible sales.
Your Next Step: Test, Measure, and Refine
The days of one-size-fits-all SEM are over. Integrating advanced mobile, geo-targeting, and remarketing strategies is the key to cutting through the noise and connecting with customers in a meaningful way.
Don’t just implement these tactics and hope for the best. The most successful marketers are those who relentlessly test, measure, and optimize. Start with a small, controlled campaign. Analyze the data, learn what works for your unique audience, and scale your successes. Your next SEM campaign could be your most profitable one yet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What’s the difference between geofencing and geo-targeting?
Geo-targeting involves showing ads to users based on their location, such as a city or ZIP code. Geofencing is more specific; it creates a virtual boundary around a precise location (like a single building), and triggers ads when a user enters that boundary. Think of geo-targeting as defining a region, while geofencing is about defining a real-time perimeter.
How far should “radius targeting” go for a local business?
This depends on your business and location. For a coffee shop in a dense urban area, a 1-2 mile radius might be sufficient. For a car dealership in a suburban area, a 10-15-mile radius could be more appropriate. Start with a reasonable estimate and analyze your campaign data to see where conversions are coming from, then adjust accordingly.
When is it better to use mobile-only targeting?
Mobile-only targeting is ideal for campaigns with goals that are best accomplished on a smartphone. This includes promoting an app, driving phone calls directly from an ad (using call extensions), or encouraging in-store visits from nearby users who are on the go.
How often should remarketing audiences be updated?
Remarketing audiences are typically updated automatically as new users visit your site. However, you should review your audience definitions and list performance quarterly. Check if the membership duration (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days) is optimal for your sales cycle and consider creating new, more segmented lists based on recent campaigns or website changes.
Learn more about: How to Combine SEM and SEO for Maximum Visibility



Leave a Reply